The Székelys or Székely (Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈseːkɛj]), sometimes also referred to as Szeklers (Hungarian: székelyek, Romanian: Secui, German: Szekler, Latin: Siculi), are a subgroup[5][6] of the Hungarian people living mostly in the Székely Land. A significant population descending from the Székelys of Bukovina lives in Tolna and Baranya counties in Hungary and in certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In 1952 the former province of Mureş (with the highest concentration of Székely population) was legally designated as the Hungarian Autonomous Region.
It was superseded in 1960 by the Mureş-Hungarian Autonomous Region,
itself divided in 1968 into three non-autonomous districts, Harghita,
Covasna and Mureş.[7]
The Székelys or Székely (Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈseːkɛj]), sometimes also referred to as Szeklers (Hungarian: székelyek, Romanian: Secui, German: Szekler, Latin: Siculi), are a subgroup[5][6] of the Hungarian people living mostly in the Székely Land. A significant population descending from the Székelys of Bukovina lives in Tolna and Baranya counties in Hungary and in certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In 1952 the former province of Mureş (with the highest concentration of Székely population) was legally designated as the Hungarian Autonomous Region.
It was superseded in 1960 by the Mureş-Hungarian Autonomous Region,
itself divided in 1968 into three non-autonomous districts, Harghita,
Covasna and Mureş.[7]In the Middle Ages, the Székelys, along with the Saxons, played a key role in the defense of the Kingdom of Hungary against the Ottomans[8] in their posture of guards of the eastern border. With the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, Transylvania (including the Székely Land) became part of Romania, and the Székely population was a target of Romanianization efforts.[9] In post-Cold War Romania, where the Székelys form roughly a half of the ethnic Hungarian population, members of the group have been among the most vocal of Hungarians seeking an autonomous Hungarian region in Transylvania.[10] They were estimated to number about 860,000 in the 1970s and are officially recognized as a distinct minority group by the Romanian government.[7] However, the Romanian government does not recognize the existence of a Székely Land.
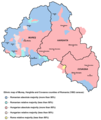
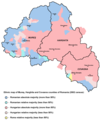
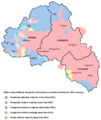
Today's Székely Land roughly corresponds to the Romanian counties of Harghita, Covasna and central and eastern Mureş. Based on the official 2011 Romanian census, 1,227,623[11] ethnic Hungarians live in Romania, mostly in the region of Transylvania making 19.6% of the population of this region. Of these, 609,033 (according to the 2011 Romanian Census) live in the counties of Harghita, Covasna and Mureş, which taken together have a Hungarian majority (58%).[12] The Hungarians in Székely Land therefore account for half (49.41%) of the Hungarians in Romania. When given the choice on the 2011 Romanian census between ethnically identifying as Székely or as Hungarian, fearing that the Romanian government would misuse the data, the overwhelming majority of the Székelys chose the latter. 532 persons declared themselves as ethnic Székely.[4]
Contents
History
Main article: History of the Székely people
The Székelys derive their name from a Hungarian expression meaning "frontier guards".[7] The Székely territories came under the leadership of the Count of the Székelys (Latin: Comes Siculorum), initially a royal appointee from the non-Székely Hungarian nobility who was de facto a margrave;
from the 15th century onward, the voivodes of Transylvania held the
office themselves. The Székelys were considered a distinct ethnic group (natio Siculica)[13] and formed part of the Unio Trium Nationum ("Union of Three Nations"), a coalition of three Transylvanian Estates, the other two "nations" being the (also predominantly Hungarian) nobility and the Saxon (that is, ethnic German)
burghers. These three groups ruled Transylvania from 1438 onward,
usually in harmony though sometimes in conflict with one another. During
the Long War, the Székelys formed an alliance with Prince Michael the Brave of Wallachia against the army of Andrew Cardinal Báthory, recently appointed Prince of Transylvania.Origins
The origin of the Székelys has been much debated. It is now generally accepted that they are descendants of Hungarians (or of Magyarized Turkic peoples) transplanted to the eastern Carpathians to guard the frontier, their name meaning simply "frontier guards".[7] The Székelys have historically claimed descent from Attila's Huns[7] (repeated in Procopius's De bello Gothico),[7] and believed they played a special role in shaping Hungary. Ancient legends recount that a contingent of Huns remained in Transylvania, later allying with the main Hungarian army that conquered the Carpathian Basin in the 9th century. The thirteenth-century chronicler Simon of Kéza also claimed that the Székely people descended from Huns who lived in mountainous lands prior to the Hungarian conquest.[14]After the theory of Hunnic descent lost scholarly currency in the 20th century two substantial ideas emerged about Székely ancestry:[15]
- Some scholars suggested that the Székelys were simply Magyars,[15] like other Hungarians, transplanted in the Middle Ages to guard the frontiers. Researches could not prove that Szeklers spoke a different language.[15] In this case, their strong cultural differences from other Hungarians stem from centuries of relative isolation in the mountains.
- Others suggested Turkic origin as Avar, Kabar or Esegel-Bulgar ancestries.[15][16]
Researches indicate that Székelys undoubtedly spoke in Hungarian.[17] Toponyms at the Székely settlement area also give proof of their Hungarian mother tongue.[17] The Székely dialect does not have more Bulgaro-Turkish loan-words derived from before the Hungarian Conquest of the Carpathian Basin than standard Hungarian does.[17] Even if the Székelys had been a Turkic stock they had to lose their original vernacular at a very early date.[17]
Demographics
The Székely live mainly in Harghita, Covasna and Mureş counties. They identify themselves as Hungarians, but they maintain a somewhat distinct ethnic identity from other Hungarians.[18] Hungarians form a majority of the population in the counties of Covasna and Harghita.| County | Hungarians | % of county population |
|---|---|---|
| Harghita | 257,707 | 84.62% |
| Covasna | 150.468 | 73.74% |
| Mureş | 200,858 | 38.09% |
Autonomy
There were Székely autonomous regions from 1952–1968. First the Magyar Autonomous Region was created in 1952, later (1960) renamed Mureş-Magyar Autonomous Region. Ever since the abolition of the Mureş-Magyar Autonomous Region by the Ceauşescu regime in 1968, some of the Székely have pressed for their autonomy to be restored. Several proposals have been discussed within the Székely Hungarian community and by the Romanian majority. One of the Székely autonomy initiatives is based on the model of the Spanish autonomous community of Catalonia.[19] A major peaceful demonstration was held in 2006 in favor of autonomy.[20] Since 2013 thousands of ethnic Hungarians march for autonomy every year on March 10 in Targu Mures, Romania. [21] March 10 is the anniversary of the execution in Targu Mures in 1854 of three Szeklers who tried to achieve national self-determination.[22]Literature
Áron Tamási, a 20th-century Székely writer from Lupeni, wrote many novels about the Székely which set universal stories of love and self-individuation against the backdrop of Székely village culture. Other Székely writers include the folklorist Elek Benedek, the novelist József Nyírő, the television and film writer Louis Székely and the poet Sándor Kányádi.[citation needed]Symbols

Flag of Székely National Council, one of the main political organizations of the Székelys[23]